
Individuals are living longer in present times due to an increase in life expectancy. Australia is therefore experiencing a rise in the ageing population as well as a surge in demand for health care services, social services, and aged care. The process of seeking appropriate aged care solutions can be stressful for both clients and their families, requiring thoughtful management of emotional pressures. Amidst these challenges, the role of financial advisers in aged care becomes central to the ongoing financial, and sometimes overall wellbeing, of clients.
The table below highlights the advice topics which clients typically seek financial advice on:
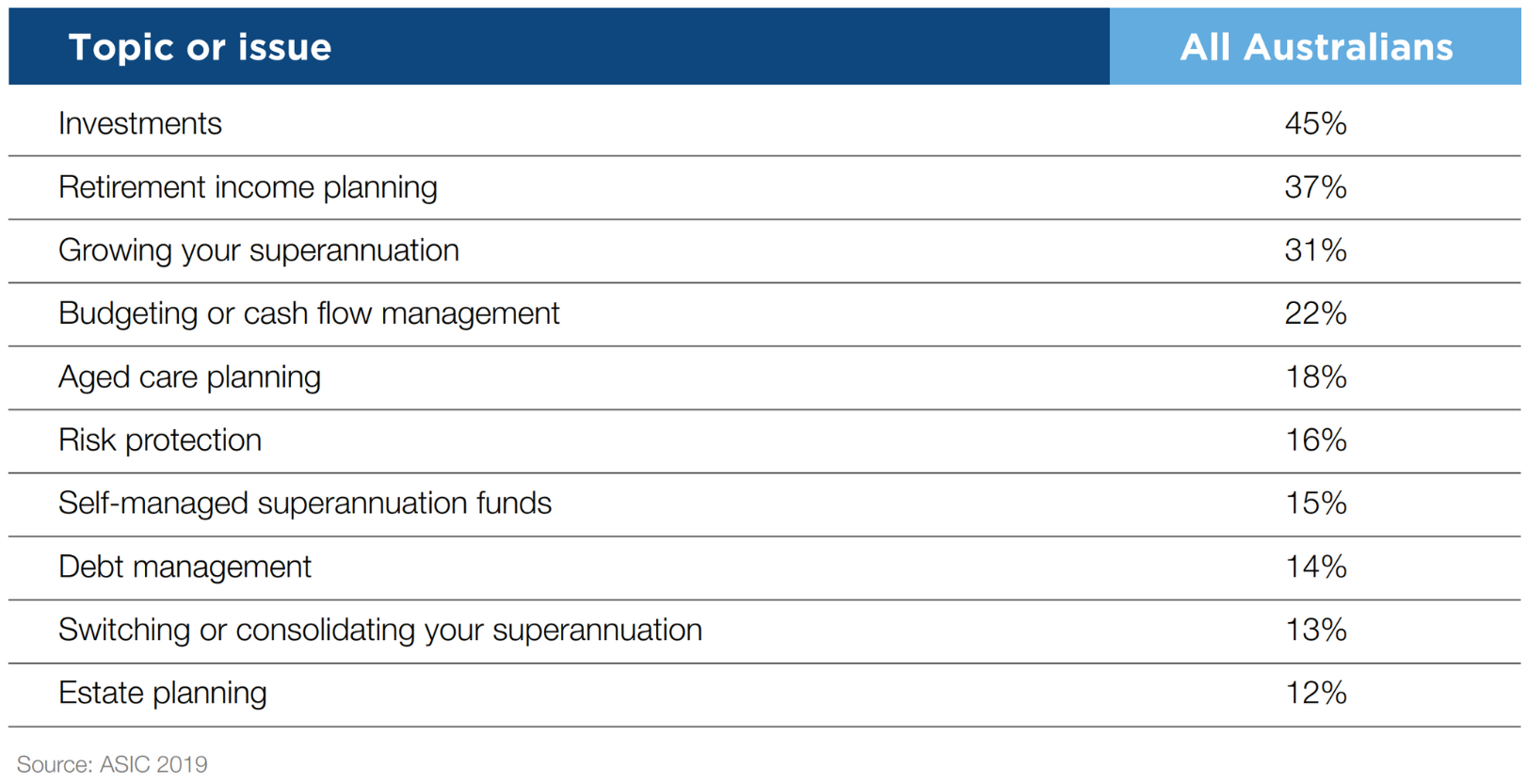
As the above table depicts, only around 18% of Australians on average seek advice on aged care. In order to improve this figure, the importance of a financial adviser needs to be understood. Every decision a clients makes about aged care has a financial component; from pensions to home care packages, from Carers Payments to Carers Supplements to Carers Allowances, from retirement villages to residential aged care. For aged care decisions, clients and their families may have the following practical and emotional questions:
- Should the family home be sold?
- If the family home is retained, what would happen to it?
- How can the costs, particularly lump sum costs for aged care accommodation, be financed?
- Can enough income be derived to cover other ongoing costs of care?
- What are the opportunities for bequests?
- Are all health care costs covered (motorised scooters, hearing aids etc.)?
- Is a power of attorney needed and what other legal issues need to be considered?
Each of these questions can be dealt with comprehensively with the help of a financial adviser, so that clients maximise their objectives without unduly sacrificing wealth. In some cases, clients will have already made decisions about these issues and will look to their advisers for verification. With the introduction of means testing based on both assets and income for some daily care fees, understanding how these decisions affect the age pension, other supplements and tax for aged care clients has become even more important. Key aspects of the financial adviser’s role are to:
- Identify financial goals and objectives
- Provide information on how aged care services will affect financial security
- Formulate strategies to achieve financial goals and objectives such as whether to sell the family home, how to best generate income, how to finance accommodation charges in an aged care facility and how to maintain Centrelink benefits
- Help aged care recipients and their familes to understand the range of care options and how the aged care system works, particularly in terms of fees and charges
- Provide support in finding and accessing the right care, or refer the client to another professional to assist, taking into account the affordability of various options
- Review estate planning needs and make referrals to tax accountants and estate planning lawyers.
In summary, a financial adviser plays a multifaceted role, addressing financial, emotional, and practical aspects to help individuals make informed decisions about their aged care needs and finances as they age. The goal is to ensure a comfortable and financially secure transition into the later stages of life, including any necessary aged care services.